








Here is Songning Lai.( You can call me Sony. )
I received my undergraduate degree from the School of Information Science and Engineering(Chongxin College), Shandong University in China,supervised by Prof. Zhi Liu. I was also an RA at HKUST@AI Thrust&INFO Hub, supervised by Prof. Yutao Yue. And now I am a Quant Researcher in JoinQuant.
My primary research interest lies in the domain of Trustworthy AI 🤖, encompassing explainability 🔍, robustness 🛡️, faithfulness ✅, and safety 🔒 of AI. Specifically, I have focused extensively on Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) within the realm of explainability. My past research includes an investigation into the robustness and generalization of CBMs in unsupervised settings (ICLR 2024), application of CBMs in multimodal contexts for unsupervised tasks (Under Review), pioneering work on continual learning with CBMs (ACM MM 2025), as well as the first exploration of CBMs in the context of security, particularly backdoor attacks (Under review 1; Under review 2). Furthermore, my research has extended to applying CBMs in medical fields (NIPS 2024; ECML 2025) and autonomous driving applications (ICRA 2025).
Beyond my work with CBMs, I have also explored issues related to robustness and faithfulness in time series (ICML 2025; ACM MM 2025,ICASSP 2026), continual learning(ACM MM25) and explainability for LLM (ICLR 2026). Prior to these endeavors, my research efforts were directed towards computer vision (Image and Vison Computing; ICASSP 2025), multimodal sentiment analysis (IJCNN 2024; Displays), and community detection (Neurocomputing).
If you are interested in any aspect of me, I would love to chat and collaborate 💬, please email me at - lais0328eee@gmail.com 📧.
🔥 News
- 01.2026 🎉 Our paper "ACE: Attribution-Controlled Knowledge Editing for Multi-hop Factual Recall" has been accepted at ICLR 2026. (CCF None)!
- 01.2026 🎉 Our paper "TOWARDS RELIABLE TIME SERIESFORECASTING UNDER FUTURE UNCERTAINTY: AMBIGUITY AND NOVELTY REJECTION MECHANISMS" has been accepted at ICASSP 2026. (CCF B)!
- 01.2026 🎉 Our paper "Towards Better Evaluation Metrics for Text-to-Motion Generation" has been accepted at ACM TheWebConf 2026 (WWW2026) Workshop TIME!
- 01.2026 🎉 Our paper "TPTD: A Tursted Privacy-Preserving Truth Discovery Scheme for Quality Enhancement in Team-based Mobile Crowd Sensing" has been accepted at Knowledge-Based Systems KBS. (IF: 7.2, JCR Q1, CCF C)!
- 12.2025 🎉 Our paper "Da Yu: Towards USV-Based Image Captioning for Waterway Surveillance and Scene Understanding" has been accepted at IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY TCSVT. (IF: 11.1, JCR Q1, CCF B)!
- 10.2025: 🎉 Our paper "Mimicking the Physicist's Eye : A VLM-centric Approach for Physics Formula Discovery" has been accepted at NeurIPS 2025 Workshop on Efficient Reasoning with spotlight!
- 10.2025: 🎉 Our paper "Orientation-Aware Detection System for Real-Time Monitoring of Cracks in Steel Structures" has been accepted at Expert Systems With Applications (JCR Q1, IF: 7.5)!
- 09.2025:🎉 Our paper "Boosting Expertise and Efficiencyin LLM:A Knowledge-Enhanced Framework for Construction Support" has been accepted at Alexandria Engineering Journal (JCR Q1, IF: 6.8)!
- 08.2025: 🎉 Our 3 papers have been accepted at ACM MM 2025 BNI Track (CCF A, oral, BNI Papers are considered outstanding ACM MM full papers, and accepted BNI papers will apear in the main proceedings)! ("Learning New Concepts, Remembering the Old: Continual Learning for Multimodal Concept Bottleneck Models"; "Physics-Informed Representation Alignment for Sparse Radio-Map Reconstruction"; "Can Audio Language Models Listen Between the Lines? A Study on Metaphorical Reasoning via Unspoken")
- 07.2025: 🎉 Our 4 papers have been accepted at ACM MM 2025 (CCF A, oral)!("From Guesswork to Guarantee: Towards Faithful Multimedia Web Forecasting with TimeSieve"; "ANT: Adaptive Neural Temporal-Aware Text-to-Motion Model"; "Text2Weight: Bridging Natural Language and Neural Network Weight Spaces"; "CFSSeg: Closed-Form Solution for Class-Incremental Semantic Segmentation of 2D Images and 3D Point Clouds")
- 07.2025: 🎉 Our paper "VQualA 2025 Challenge on Face Image Quality Assessment: Methods and Results" has been accepted at ICCV 2025 workshop VQualA!
- 07.2025: 🎉 Our paper "Generative Knowledge-Guided Review System for Construction Disclosure Documents" has been accepted at Advanced engineering informatics (JCR Q1, IF: 9.9)!
- 06.2025: 🎉 Our paper "Automated Detection of Complex Construction Scenes Using a Lightweight Transformer-based Method" has been accepted at Automation in Construction (JCR Q1, IF:9.6)!
- 05.2025: 🎉 Our paper "Stable Vision Concept Transformers for Medical Diagnosis" has been accepted at ECML-PKDD 2025 (CCF B)!
- 04.2025: 🎉 Our paper "IMTS is Worth Time X Channel Patches: Visual Masked Autoencoders for Irregular Multivariate Time Series Prediction" has been accepted by ICML 2025 (CCF A)!
- 04.2025: 🎉 Our paper "Class Incremental Semantic Segmentation Based on Linear Closed-form Solution" has been accepted by CVPR 2025 workshop BASE!
- 04.2025: 🎉 Our paper "Beyond Patterns: Harnessing Causal Logic for Autonomous Driving Trajectory Prediction" has been accepted by IJCAI 2025 (CCF A)!
- 02.2025: 🎉 Our paper "Enhancing domain adaptation for plant diseases detection through Masked Image Consistency in Multi-Granularity Alignment" has been accepted by Expert Systems With Applications (JCR Q1, IF:8.4, CCF C).
- 01.2025: 🎉 Our paper "Dependable Robust Interpretable Visionary Ensemble Framework in Autonomous Driving" has been accepted by ICRA 2025 (CCF B)!
- 12.2024: 🎉 Our paper "PEPL:Precision-Enhanced Pseudo-Labeling forFine-Grained lmage Classification inSemi-Supervised Learning" has been accepted at ICASSP 2025 (CCF B)!
- 09.2024: 🎉 Our paper "Towards Multi-dimensional Explanation Alignment for Medical Classification" has been accepted by (NeurIPS 2024) (CCF A)!
- 07.2024: 🎉 Our paper "FTS: A Framework to Find a Faithful TimeSieve" has been accepted by IJCAI 2024 workshop.
- 06.2024: 🎉 Our paper "A Comprehensive Review of Community Detection in Graphs" has been accepted by Neurocomputing(JCR Q1; CCF C).
- 03.2024: 🎉I am awarded the honor of excellent graduate of Shandong Province and excellent graduate of Shandong University.
- 03.2024: 🎉 Our paper on Multimodal Sentiment Analysis has been accepted by IJCNN2024(CCF C).
- 01.2024: 🎉 Our paper "Faithful Vision-Language Interpretation via Concept Bottleneck Models" has been accepted at The 12th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2024)!.
- 10.2023: 🎉 Our paper "Multimodal sentiment analysis: A survey" has been accepted by the journal Displays (JCR Q1).
- 10.2023: 🎉 Our paper "Cross-domain car detection model with integrated convolutional block attention mechanism" has been accepted by the journal Image and Vison Computing (JCR Q1; CCF C).
- 11.2022: 🎉Get the First Prize in Contemporary Undergraduate Mathematical Contest in Modeling National (top 0.6%).
- 11.2022: 🎉I am very glad to give an oral report at the international conference CISP-BMEI 2022 and win the Best Paper Award.
- 10.2022: 🎉 Our paper "Predicting lysine phosphoglycerylation sites using bidirectional encoder representations with transformers & protein feature extraction and selection" has been accepted by CISP-BMEI 2022 (Tsinghua B)
📝 Publications (Selected)
2026
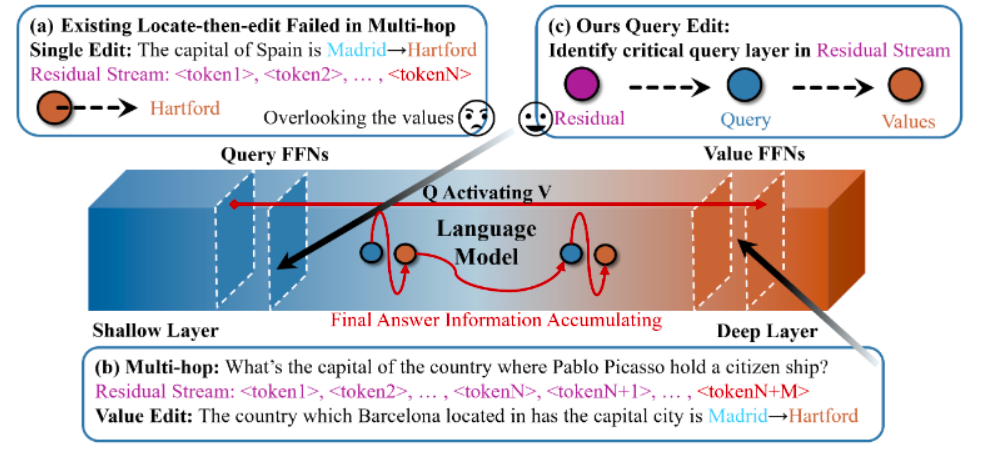
ACE: Attribution-Controlled Knowledge Editing for Multi-hop Factual Recall
Jiayu Yang†, Yuxuan Fan†, Songning Lai†, Shengen Wu, Jiaqi Tang, Chun Kang, Zhijiang Guo, Yutao Yue.
International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR2026 CCF None Top Tier Core A*.
In this paper, we propose ACE, a knowledge editing framework based on neuron attribution control. By locating and correcting the key neuron pathways in the Transformer internal inference chain, ACE solves the problem of intermediate implicit subject failure when multi-hop knowledge updating in large language models, and reveals the cognitive mechanism of query neuron driving semantic accumulation.
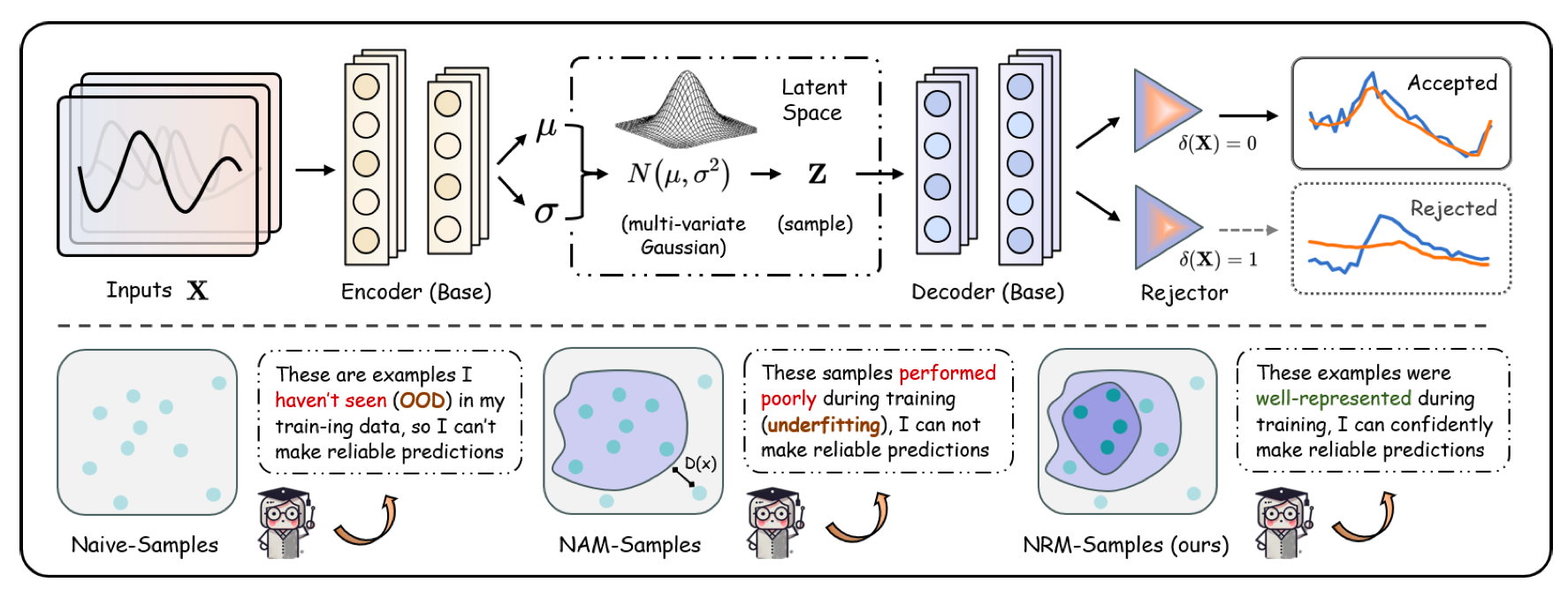
Ninghui Feng†, Songning Lai†, Xin Zhou, Jiayu Yang, Kunlong Feng, Zhenxiao Yin, Fobao Zhou, Zhangyi Hu, Yutao Yue, Yuxuan Liang, Boyu Wang, Hang Zhao
The Conference on ICASSP 2026 CCF B Core A.
We propose a dual rejection framework combining ambiguity rejection (using prediction error variance) and novelty rejection (leveraging VAEs and Mahalanobis distance) to enhance time series forecasting reliability by abstaining from low-confidence predictions and detecting distribution shifts, effectively reducing errors in dynamic environments. This approach addresses underfitting and out-of-distribution challenges without requiring future ground truth, advancing robust forecasting in complex real-world scenarios.
2025
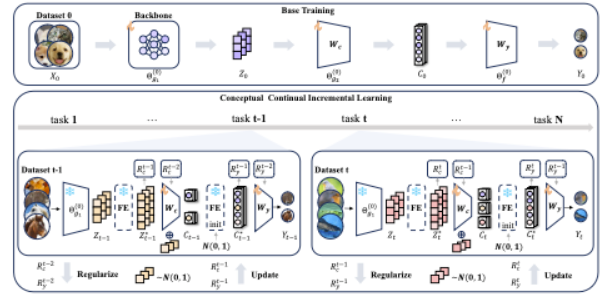
Songning Lai, Mingqian Liao, Zhangyi Hu, Jiayu Yang, Wenshuo Chen, Hongru Xiao, Jianheng Tang, Haicheng Liao, Yutao Yue~
The Conference on ACM MM 2025 BNI Track CCF A Top Tier Core A* Oral Outstanding.
This paper defines the continuous learning problem of CBM for the first time, and proposes a framework CONCIL to continuously learn concept and label simultaneously. Theoretical and experimental results verify the efficiency and absolute memory property of the framework.
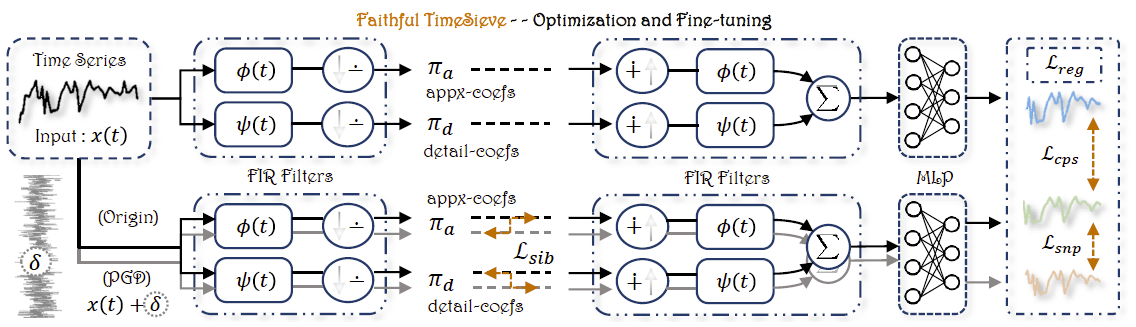
From Guesswork to Guarantee: Towards Faithful Multimedia Web Forecasting with TimeSieve
Songning Lai, Ninghui Feng, Jiechao Gao, Hao Wang, Haochen Sui, Xin Zou, Jiayu Yang, Wenshuo Chen, Lijie Hu, Hang Zhao, Xuming Hu, Yutao Yue
The Conference on ACM MM 2025 CCF A Top Tier Core A*.
We propose Faithful TimeSieve (FTS), an enhanced framework that systematically detects and mitigates unfaithfulness in TimeSieve (sensitivity to random seeds, input/layer/parameter perturbations), improving prediction reliability and robustness for multimedia web forecasting. FTS achieves SOTA on multiple benchmarks while significantly improving stability and consistency.
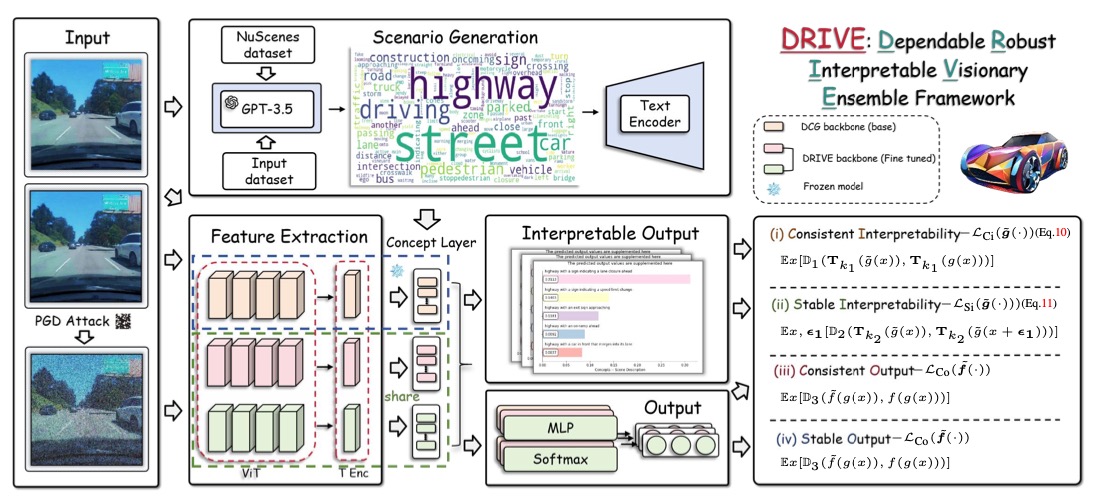
DRIVE: Dependable Robust Interpretable Visionary Ensemble Framework in Autonomous Driving
Songning Lai, Tianlang Xue, Hongru Xiao, Lijie Hu, Jiemin Wu, Ruiqiang Xiao, Ninghui Feng, Haicheng Liao, Zhenning Yang, Yutao Yue~
The Conference on ICRA 2025 CCF B Core A*.
We introduce DRIVE, a framework designed to enhance the dependability and stability of explanations in end-to-end unsupervised autonomous driving models, addressing instability issues and improving trustworthiness through consistent and stable interpretability and output, as demonstrated by empirical evaluations. This framework provides novel metrics for assessing the reliability of concept-based explainable autonomous driving systems, advancing their real-world deployment.
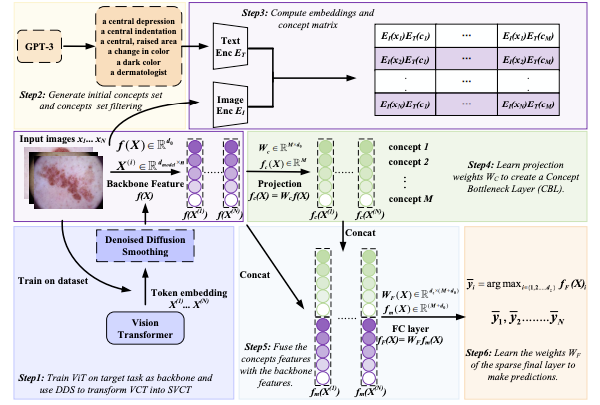
Stable Vision Concept Transformers for Medical Diagnosis
Lijie Hu†, Songning Lai†, Yuan Hua, Shu Yang, Jingfeng Zhang, Di Wang
The Conference on ECML-PKDD 2025 CCF B Core A.
The paper introduces Vision Concept Transformer (VCT) and its stable variant SVCT, which integrate vision transformers with concept features and denoised diffusion smoothing to preserve medical imaging accuracy while providing robust, interpretable explanations resilient to perturbations.
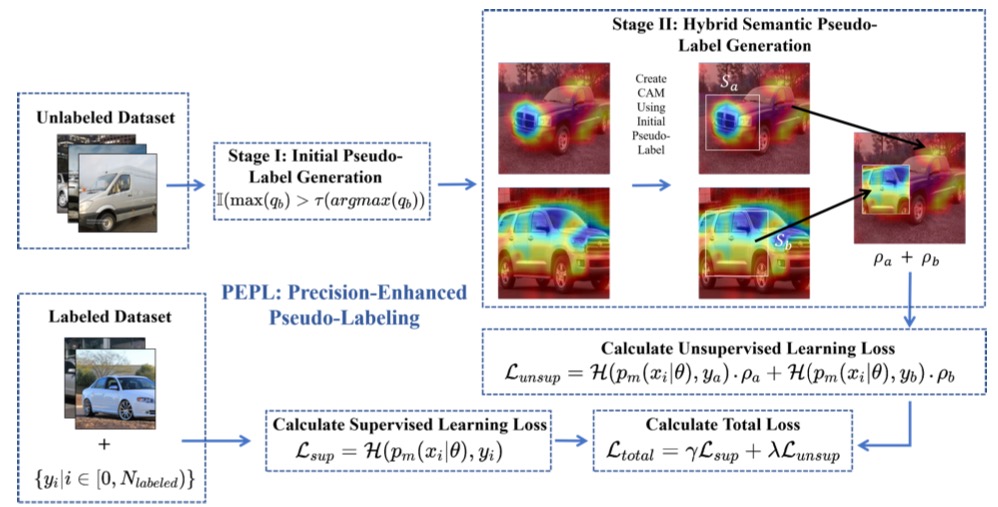
Bowen Tian†, Songning Lai†, Lujundong Li, Zhihao Shuai, Runwei Guan, Tian Wu, Yutao Yue~
The Conference on ICASSP 2025 CCF B Core B.
We introduce Precision-Enhanced Pseudo-Labeling (PEPL), a semi-supervised learning approach for fine-grained image classification that generates and refines pseudo-labels using Class Activation Maps (CAMs) to capture essential details, significantly improving accuracy and robustness over existing methods on benchmark datasets. The approach consists of initial and semantic-mixed pseudo-label generation phases to enhance the quality of labels and has been open-sourced for public use.
2024
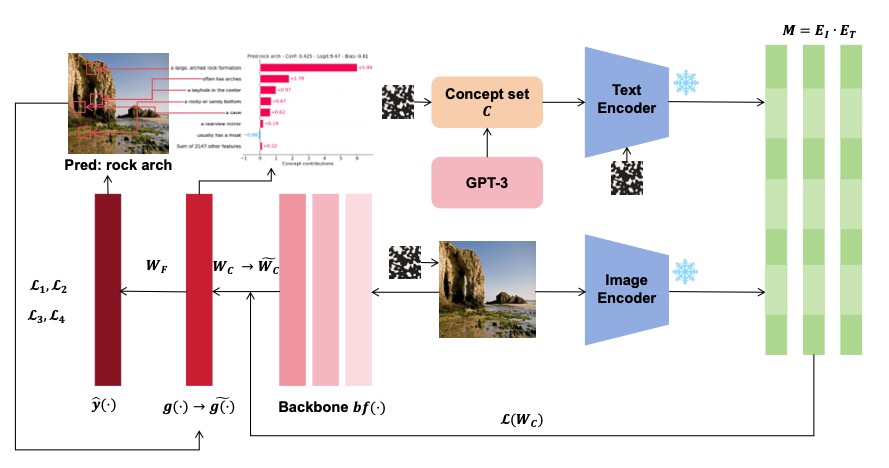
Faithful Vision-Language Interpretation via Concept Bottleneck Models
Songning Lai, Lijie Hu, Junxiao Wang, Laure Berti and Di Wang
The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR2024 CCF None Top Tier Core A*.
We introduce the Faithful Vision-Language Concept (FVLC) model, addressing the instability of label-free Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs). Our FVLC model demonstrates superior stability against input and concept set perturbations across four benchmark datasets, with minimal accuracy degradation compared to standard CBMs, offering a reliable solution for model interpretation.
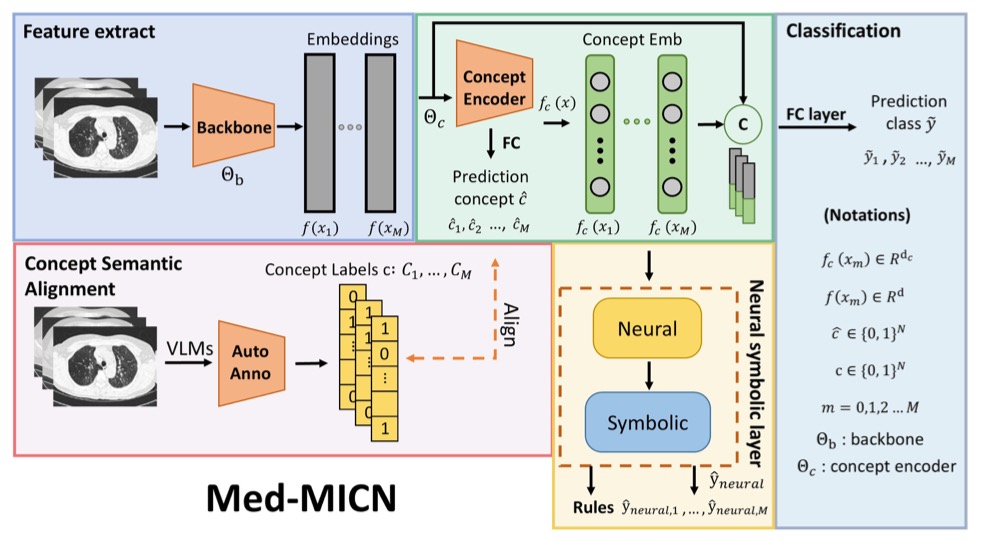
Towards Multi-dimensional Explanation Alignment for Medical Classification
Lijie Hu†, Songning Lai†, Wenshuo Chen† (equal contribution), Hongru Xiao, Hongbin Lin, Lu Yu, Jingfeng Zhang, and Di Wang
The Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems NeurIPS 2024 CCF A Top Tier Core A*.
We proposed an end-to-end framework called Med-MICN, which leverages the strength of different XAI methods such as concept-based models, neural symbolic methods, saliency maps, and concept semantics. Our outputs are interpreted in multiple dimensions, including concept prediction, saliency maps, and concept reasoning rules, making it easier for experts to identify and correct errors. Med-MICN demonstrates superior performance and interpretability compared with other concept-based models and the black-box model baselines.
📚 Complete Publications
2026
- ACE: Attribution-Controlled Knowledge Editing for Multi-hop Factual Recall, Jiayu Yang†, Yuxuan Fan†, Songning Lai†, Shengen Wu, Jiaqi Tang, Chun Kang, Zhijiang Guo, Yutao Yue, ICLR 2026 (CCF None).
- TOWARDS RELIABLE TIME SERIESFORECASTING UNDER FUTURE UNCERTAINTY: AMBIGUITY AND NOVELTY REJECTION MECHANISMS, Ninghui Feng†, Songning Lai†, Xin Zou, ...,Hang Zhao, ICASSP 2026 (CCF B).
- TPTD: A Tursted Privacy-Preserving Truth Discovery Scheme for Quality Enhancement in Team-based Mobile Crowd Sensing, Yajiang Huang, ..., Songning Lai, ..., Houbing Herbert Song, Knowledge-Based Systems(KBS) (JCR Q1, IF: 7.2).
2025
- Learning New Concepts, Remembering the Old: Continual Learning for Multimodal Concept Bottleneck Models, Songning Lai, Mingqian Liao, Zhangyi Hu, Jiayu Yang, Wenshuo Chen, Hongru Xiao, Jianheng Tang, Haicheng Liao, Yutao Yue, ACM MM 2025 Brave New Idea Track (CCF A, Core A*) <BNI Papers are considered outstanding ACM MM full papers, and accepted BNI papers will apear in the main proceedings>.
- From Guesswork to Guarantee: Towards Faithful Multimedia Web Forecasting with TimeSieve, Songning Lai, Ninghui Feng, Jiechao Gao, Hao Wang, Haochen Sui, Xin Zou, Jiayu Yang, Wenshuo Chen, Hang Zhao, Xuming Hu, Yutao Yue, ACM MM 2025 (CCF A, Core A*).
- DRIVE: Dependable Robust Interpretable Visionary Ensemble Framework in Autonomous Driving, Songning Lai, Ninghui Feng, Jiechao Gao, Hao Wang, Haochen Sui, Xin Zou, Jiayu Yang, Wenshuo Chen, Hang Zhao, Xuming Hu, Yutao Yue, ICRA 2025 (CCF B, Core A*).
- Stable Vision Concept Transformers for Medical Diagnosis, Lijie Hu†, Songning Lai†, Yuan Hua†, Jingfeng Zhang, Pan Zhou, Di Wang, ECML-PKDD 2025 (CCF B, Core A).
- PEPL: Precision-Enhanced Pseudo-Labeling for Fine-Grained Image Classification in Semi-Supervised Learning, Bowen Tian†, Songning Lai†, Lujundong Li, Zhihao Shuai, Runwei Guan, Tian Wu, Yutao Yue, ICASSP 2025 (CCF B, Core B).
- IMTS is Worth Time X Channel Patches: Visual Masked Autoencoders for Irregular Multivariate Time Series Prediction, Zhangyi Hu, Jiemin Wu, Hua Xu, Minqian Liao, Ninghui Feng, Bo Gao, Songning Lai, Yutao Yue, ICML 2025 (CCF A, Core A*).
- Physics-Informed Representation Alignment for Sparse Radio-Map Reconstruction, Jia Haozhe, Wenshuo Chen, Huang Zhihui, Lei Wang, Hongru Xiao, Jia Nanqian, Keming Wu, Songning Lai, Bowen Tian, Yutao Yue, ACM MM 2025 Brave New Idea Track (CCF A, Core A*) <BNI Papers are considered outstanding ACM MM full papers, and accepted BNI papers will apear in the main proceedings>.
- Can Audio Language Models Listen Between the Lines? A Study on Metaphorical Reasoning via Unspoken, Hongru Xiao, Xiang Li, Duyi Pan, Longfei Zhang, ZhixueSong, Jiale Han, Songning Lai, Wenshuo Chen, Jing Tang, Benyou Wang, ACM MM 2025 Brave New Idea Track (CCF A, Core A*) <BNI Papers are considered outstanding ACM MM full papers, and accepted BNI papers will apear in the main proceedings>.
- IMTS is Worth Time X Channel Patches: Visual Masked Autoencoders for Irregular Multivariate Time Series Prediction, Zhangyi Hu, Jiemin Wu, Hua Xu, Minqian Liao, Ninghui Feng, Bo Gao, Songning Lai, Yutao Yue, ICML 2025 (CCF A, Core A*).
- ANT: Adaptive Neural Temporal-Aware Text-to-Motion Model, Wenshuo Chen, Kuimou Yu, Jia Haozhe, Kaishen Yuan, Zexu Huang, Bowen Tian, Songning Lai, Hongru Xiao, Erhang Zhang, Lei Wang, Yutao Yue, ACM MM 2025 (CCF A, Core A*).
- Text2Weight: Bridging Natural Language and Neural Network Weight Spaces, Bowen Tian, Wenshuo Chen, Zexi Li, Songning Lai, Jiemin Wu, Yutao Yue, ACM MM 2025 (CCF A, Core A*).
- CFSSeg: Closed-Form Solution for Class-Incremental Semantic Segmentation of 2D Images and 3D Point Clouds, Jiaxu Li, Rui Li, Jianyu Qi, Songning Lai, Linpu Lv, Kejia Fan, Jianheng Tang, Yutao Yue, Dongzhan Zhou, Yunhuai Liu, Huiping Zhuang, ACM MM 2025 (CCF A, Core A*).
- Beyond Patterns: Harnessing Causal Logic for Autonomous Driving Trajectory Prediction, Bonan Wang, Haicheng Liao, Chengyue Wang, Bin Rao, Yanchen Guan, Guyang Yu, Jiaxun Zhang, Songning Lai, Chengzhong Xu, Zhenning Li, IJCAI 2025 (CCF A, Core A*).
- Boosting Expertise and Efficiencyin LLM:A Knowledge-Enhanced Framework for Construction Support, Bin Yang, Hongru Xiao, Zixuan Zenga, Songning Lai, Jiale Han, Yanke Tana and Yiqing Ni, Expert Systems With Applications (JCR Q1, IF:8.4, CCF C).
- Boosting Expertise and Efficiencyin LLM:A Knowledge-Enhanced Framework for Construction Support, Hongru Xiao, ..., Songning Lai, Alexandria Engineering Journal (JCR Q1, IF: 6.8)!
- Generative Knowledge-Guided Review System for Construction Disclosure Documents, Hongru Xiao, Jiankun Zhuanga, Bin Yanga, Jiale Hanb, Yantao Yu and Songning Lai, Advanced engineering informatics (JCR Q1, IF: 9.9, CCF B).
- Automated Detection of Complex Construction Scenes Using a Lightweight Transformer-based Method, Hongru Xiao, Bin Yang, Yujie Lu, Wenshuo Chen, Songning Lai, Biaoli Gao, Automation in Construction (JCR Q1, IF:9.6).
- Enhancing domain adaptation for plant diseases detection through Masked Image Consistency in Multi-Granularity Alignment, Guinan Guo, Songning Lai, Qingyang Wu, Yuntao Shou, Wenxu Shi, Expert Systems With Applications (JCR Q1, IF:8.4, CCF C).
- Da Yu: Towards USV-Based Image Captioning for Waterway Surveillance and Scene Understanding, Runwei Guan, ...., Songning Lai, ... ,Hui Xiong, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY TCSVT. (IF: 11.1, JCR Q1, CCF B)
2024
- Faithful Vision-Language Interpretation via Concept Bottleneck Models, Songning Lai, Lijie Hu, Junxiao Wang, Laure Berti and Di Wang, The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR2024(CCF None).
- Towards Multi-dimensional Explanation Alignment for Medical Classification, Lijie Hu†, Songning Lai†, Wenshuo Chen†, Hongru Xiao, Hongbin Lin, Lu Yu, Jingfeng Zhang, and Di Wang, The Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems NeurIPS 2024(CCF A).
- Shared and private information learning in multimodal sentiment analysis with deep modal alignment and self-supervised multi-task learning, Songning La†, Jiakang Li, Guinan Guo, Xifeng Hu, Yulong Li, Yuan Tan, Zichen Song, Yutong Liu, Zhaoxia Ren~, Chun Wang~, Danmin Miao~ and Zhi Liu~, International Joint Conference on Neural Networks IJCNN 2024(CCF C).
- A Comprehensive Review of Community Detection in Graphs, Jiakang Li†, Songning Lai†, Zhihao Shuai, Yuan Tan, Yifan Jia, Mianyang Yu, Zichen Song, Xiaokang Peng, Ziyang Xu, Yongxin Ni, Haifeng Qiu, Jiayu Yang, Yutong Liu, Yonggang Lu~, Neurocomputing (JCR Q1 (IF: 6.0) CCF C).
- Multimodal Sentiment Analysis: A Survey, Songning Lai, Haoxuan Xu, Xifeng Hu, Zhaoxia Ren~ and Zhi Liu~, Displays (JCR Q1 (IF: 4.3)).
- Cross-domain car detection model with integrated convolutional block attention mechanism, Haoxuan Xu†, Songning Lai† and Yang Yang~, Image and Vision Computing (JCR Q1 (IF:4.7) CCF C).
- Predicting Lysine Phosphoglycerylation Sites using Bidirectional Encoder Representations with Transformers & Protein Feature Extraction and Selection, Songning Lai, Xifeng Hu, Jing Han, Chun Wang, Subhas Mukhopadhyay, Zhi Liu~ and Lan Ye~, 2022 15th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics CISP-BMEI 2022(Tsinghua B).
🎖 Honors and Awards
Including academic competition, social practice, innovation and entrepreneurship, sports, aesthetic education, volunteer, scholarship and other aspects
📖 Educations and Experiences
💻 Internships
🧑🤝🧑 Friends
💬 留言板 / Guestbook
欢迎留下你的想法、建议或祝福!你可以:
- 💬 分享你的想法和反馈
- 🎉 留下祝福和鼓励
- 🤝 提出合作或交流建议
- 📝 分享你的学术见解
注意:留言功能需要 GitHub 账号登录。如果你还没有启用 GitHub Discussions,请按照下面的说明进行配置。
